A snapshot on Information & Communication Technologies
in Clinical Trials
- ICT (information and communications technologies) is an umbrella term that includes any communication device or application, encompassing: radio, television, cellular phones, computer and network hardware and software as well as the various services and applications associated with them, such as videoconferencing and distance learning. ICT are now present in our daily life. The technique, this extension of the human body, needs a supplement soul, as indicated Bergson, and now puts service to the world of health and especially of brain pathologies. In 2013 and 2014 the Innovation Alzheimer Workshop provided recommendation for the use of ICT in Alzheimer disease’s and related disorders (2013 article / 2014 article). In 2014, participants of the Workshop worked more specifically on the interest of ICT in research and most particularly for clinical trials. This document is a snapshot aiming at highlighting the most important topics to be debated. Information on definitions, scientific literature and survey results are provided according to the point of view of clinicians and other stakeholders working in the field. Do not hesitate to tell us your point of view and to add relevant information in order to update this document .
This document as been prepared by Valeria Manera, Guillaume Sacco, Alexandra Konig, Cassandre Landes, Justine Lemaire, Renaud David, David Bensamoun, François Bremond, Philippe Robert.
- Clinical Trials aim at evaluating the effectiveness and safety of medications or medical devices by monitoring their effects on large groups of people. Such prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants are designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought.
- Clinical research: Clinical research is a branch of healthcare science aiming to improve knowledge of either disease or therapeutic. Clinical research may address purely biological, but also the objectives of human and social sciences. Clinical research also aims to determine the safety and effectiveness of medications, devices, diagnostic products and treatment regimens intended for human use.
- Translational Research: Translational research applies findings from basic science to enhance human health and well-being. For example, in medicine and nursing, it aims to « translate » findings in basic research into medical and nursing practice and meaningful health outcomes.
- Basic research: is a systematic study directed toward greater knowledge or understanding of the fundamental aspects of phenomena.
The different stage of clinical trials and the role of ICT :
– INVESTIGATOR’S TRAINING
– RECRUITMENT OF PARTICIPANTS
– ASSESSMENTS
– DATA ENTRY
INVESTIGATOR’S TRAINING
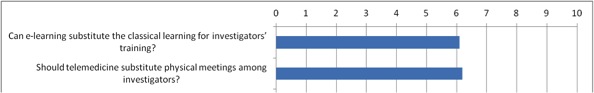
E-trainings for clinical trials are routinely used by top pharmaceutical companies and CROs in order to train the investigators and evaluate their competence and knowledge of the study procedures. Vote
Advantages
Easy to harmonize study procedures across sites
Lower cost
Less time consuming
Possibility to repeat the training, also for investigators entering an ongoing trial
Trainings available in long term
Easy to adapt to the different languages / professional figures
Possibility to show test and procedures
Lower risk of bias due to procedure misunderstanding
Disadvantages
No personal interactions with study coordinators
No immediate question feedback
Technical and connection problems
Possibility to cheat and ask others to do the training/tests
Reticence of the investigators to be evaluated
Risk of work overload due to investigator’s formal evaluation
Less adapted to the ‘to do’ skills
Results of the votes (scale 0 – 10, from totally disagree to totally agree)
31 participants:
11 clinical domain (psychologist, MD)
3 researchers
2 ICT engineers
5 Business domain (pharmaceutical industry’s)
10 undergraduate student in medicine
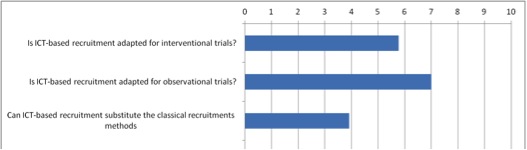
RECRUITMENT OF PARTICIPANTS
- ICT can be employed in two ways:
- To recruit through existing databases, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR)
EHR are more and more employed in public and private practices. This can help patient recruitment, because databases can be used to screen eligible patients (inclusion and exclusion criteria).
References :
http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db143.htm
http://www.healthit.gov/sites/default/files/highlights_accomplishments_ehr_adoptionsummer2012_2.pdf
http://www.healthit.gov/sites/default/files/oncdatabrief9final.pdf
http://www.slideshare.net/logicaplc/market-study-of-electronic-medical-record-emr-systems-in-europe
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Faster recruitment | Information incomplete/ incorrect |
| Many available data | Selection bias (only patients already in the database) |
| Big databases available | Data security and protection issues (who can access the data?) |
| Data easier to manage | Information not in the correct format (e.g., scanned docs) |
- E-recruitment
- Nearly 100% of the studies conducted outside of North America use only standard approaches.
- In North America, 14% of studies rely on e-recruiting
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Big population reachable through social media | Data accuracy |
| Fast recruitment | Selection bias (only participants using the internet, only interested participants) |
| Motivated and interested participants | Cloud security |
| Participants not available in existing databases (e.g., healty controls) |
References :
http://www.paconsulting.com/our-thinking/enhancing-clinical-trial-recruitment-using-social-intelligence/
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1540-4560.00254/abstract?
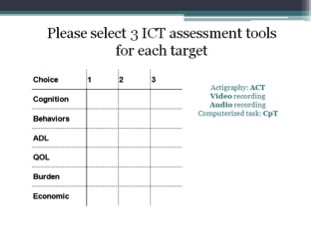
ASSESSMENTS
ClinicalTrials.gov – a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world – contains at present (January 2015) more than 2500 clinical trials involving participants with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), AD or other dementia types. We performed a keyword based search on these trials focusing on automated audio and video analysis techniques, actigraphy and computerized testing.
Keywords :
“audio analysis”, “speech analysis”, “audio recording”, “voice recording”,“voice recognition”, “video recording”, “video recognition”, “video analysis”, “3D recognition”, “accelerometer”, “actigraph” “actigraphy”, “motion sensor”, “computerized test/testing”, “computer test/testing”
Number of pharmacological clinical trials retrieved on clinicaltrials.gov
Actigraphy :
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Objective and quantitative measures | Data difficult to interpret |
| Non invasive | Data concerning motion only |
| Cheap and easy to use | Equipment failure |
| Useful for monitoring over-time | Data accuracy (for smart watch) |
Computerized testing :
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Results immediately available | Requires web connection |
| Easy to measures reaction times | Equipment failure |
| Easy to administer at home | No clinician looking at test performance |
| Easy to use | Patients not familiar with keyboard/mouse/touchscreens |
| Inexpensive equipments | Some tests difficult to administer |
Audio and video analysis :
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Unbiased, objective results | Need to follow precise study protocols |
| Quantitative measures usually not available to the clinician | Equipment failure and data loss |
| Inexpensive devices, non invasive | Ethics/Privacy issues |
| More and more algorithms for data analysis | Cloud security |
Results of the votes :
DATA ENTRY
- Top pharmaceutical companies and CROs (such as GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis) use eCRF in 100% of their trials.
- 2008 – 2009: 45% of small CRO used eCRF in more than 50% of their trials (Europe and Canada)
- There is evidence that studies employing eCRF are less expensive and require less time compared to study using the paper version of the eCRF (e.g., Le Jeannic et al., 2014)
- eCRF are regulated by FDA and EMEA, and has to follow strict rules concerning data security, data storage and data control
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2732224/
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidancecomplianceregulatoryinformation/guidances/ucm328691.pdf
http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0025348
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19345286
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1551714409000445
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2288/14/7
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Faster and cheaper studies | Require web connection |
| No need to re-input data, reduced risk of errors | Equipment failure and risk of data loss |
| Data immediately accessible to different people/entities | Inflexible procedure |
| Many clinical centers require also a paper version | |
| Cloud security |